ploeh blog danish software design
In the long run
Software design decisions should be time-aware.
A common criticism of modern capitalism is that maximising shareholder value leads to various detrimental outcomes, both societal, but possibly also for the maximising organisation itself. One major problem is when company leadership is incentivised to optimise stock market price for the next quarter, or other short terms. When considering only the short term, decision makers may (rationally) decide to sacrifice long-term benefits for short-term gains.
We often see similar behaviour in democracies. Politicians tend to optimise within a time frame that coincides with the election period. Getting re-elected is more important than good policy in the next period.
These observations are crude generalisations. Some democratic politicians and CEOs take longer views. Inherent in the context, however, is an incentive to short-term thinking.
This, it strikes me, is frequently the case in software development.
Particularly in the context of scrum there's a focus on delivering at the end of every sprint. I've observed developers and other stakeholders together engage in short-term thinking in order to meet those arbitrary and fictitious deadlines.
Even when deadlines are more remote than two weeks, project members rarely think beyond some perceived end date. As I describe in Code That Fits in Your Head, a project is rarely is good way to organise software development work. Projects end. Successful software doesn't.
Regardless of the specific circumstances, a too myopic focus on near-term goals gives you an incentive to cut corners. To not care about code quality.
...we're all dead #
As Keynes once quipped:
"In the long run we are all dead."
Clearly, while you can be too short-sighted, you can also take too long a view. Sometimes deadlines matter, and software not used makes no-one happy.
Working software remains the ultimate test of value, but as I've tried to express many times before, this does not imply that anything else is worthless.
You can't measure code quality. Code quality isn't software quality. Low code quality slows you down, and that, eventually, costs you money, blood, sweat, and tears.
This is, however, not difficult to predict. All it takes is a slightly wider time horizon. Consider the impact of your decisions past the next deadline.
Conclusion #
Don't be too short-sighted, but don't forget the immediate value of what you do. Your decisions matter. The impact is not always immediate. Consider what consequences short-term optimisations may have in a longer perspective.
The IO monad
The IO container forms a monad. An article for object-oriented programmers.
This article is an instalment in an article series about monads. A previous article described the IO functor. As is the case with many (but not all) functors, this one also forms a monad.
SelectMany #
A monad must define either a bind or join function. In C#, monadic bind is called SelectMany. In a recent article, I gave an example of what IO might look like in C#. Notice that it already comes with a SelectMany function:
public IO<TResult> SelectMany<TResult>(Func<T, IO<TResult>> selector)
Unlike other monads, the IO implementation is considered a black box, but if you're interested in a prototypical implementation, I already posted a sketch in 2020.
Query syntax #
I have also, already, demonstrated syntactic sugar for IO. In that article, however, I used an implementation of the required SelectMany overload that is more explicit than it has to be. The monad introduction makes the prediction that you can always implement that overload in the same way, and yet here I didn't.
That's an oversight on my part. You can implement it like this instead:
public static IO<TResult> SelectMany<T, U, TResult>( this IO<T> source, Func<T, IO<U>> k, Func<T, U, TResult> s) { return source.SelectMany(x => k(x).Select(y => s(x, y))); }
Indeed, the conjecture from the introduction still holds.
Join #
In the introduction you learned that if you have a Flatten or Join function, you can implement SelectMany, and the other way around. Since we've already defined SelectMany for IO<T>, we can use that to implement Join. In this article I use the name Join rather than Flatten. This is an arbitrary choice that doesn't impact behaviour. Perhaps you find it confusing that I'm inconsistent, but I do it in order to demonstrate that the behaviour is the same even if the name is different.
The concept of a monad is universal, but the names used to describe its components differ from language to language. What C# calls SelectMany, Scala calls flatMap, and what Haskell calls join, other languages may call Flatten.
You can always implement Join by using SelectMany with the identity function:
public static IO<T> Join<T>(this IO<IO<T>> source) { return source.SelectMany(x => x); }
In C# the identity function is idiomatically given as the lambda expression x => x since C# doesn't come with a built-in identity function.
Return #
Apart from monadic bind, a monad must also define a way to put a normal value into the monad. Conceptually, I call this function return (because that's the name that Haskell uses). In the IO functor article, I wrote that the IO<T> constructor corresponds to return. That's not strictly true, though, since the constructor takes a Func<T> and not a T.
This issue is, however, trivially addressed:
public static IO<T> Return<T>(T x) { return new IO<T>(() => x); }
Take the value x and wrap it in a lazily-evaluated function.
Laws #
While IO values are referentially transparent you can't compare them. You also can't 'run' them by other means than running a program. This makes it hard to talk meaningfully about the monad laws.
For example, the left identity law is:
return >=> h ≡ h
Note the implied equality. The composition of return and h should be equal to h, for some reasonable definition of equality. How do we define that?
Somehow we must imagine that two alternative compositions would produce the same observable effects ceteris paribus. If you somehow imagine that you have two parallel universes, one with one composition (say return >=> h) and one with another (h), if all else in those two universes were equal, then you would observe no difference in behaviour.
That may be useful as a thought experiment, but isn't particularly practical. Unfortunately, due to side effects, things do change when non-deterministic behaviour and side effects are involved. As a simple example, consider an IO action that gets the current time and prints it to the console. That involves both non-determinism and a side effect.
In Haskell, that's a straightforward composition of two IO actions:
> h () = getCurrentTime >>= print
How do we compare two compositions? By running them?
> return () >>= h 2022-06-25 16:47:30.6540847 UTC > h () 2022-06-25 16:47:37.5281265 UTC
The outputs are not the same, because time goes by. Can we thereby conclude that the monad laws don't hold for IO? Not quite.
The IO Container is referentially transparent, but evaluation isn't. Thus, we have to pretend that two alternatives will lead to the same evaluation behaviour, all things being equal.
This property seems to hold for both the identity and associativity laws. Whether or not you compose with return, or in which evaluation order you compose actions, it doesn't affect the outcome.
For completeness sake, the C# implementation sketch is just a wrapper over a Func<T>. We can also think of such a function as a function from unit to T - in pseudo-C# () => T. That's a function; in other words: The Reader monad. We already know that the Reader monad obeys the monad laws, so the C# implementation, at least, should be okay.
Conclusion #
IO forms a monad, among other abstractions. This is what enables Haskell programmers to compose an arbitrary number of impure actions with monadic bind without ever having to force evaluation. In C# it might have looked the same, except that it doesn't.
Next: Test Data Generator monad.
Adding NuGet packages when offline
A fairly trivial technical detective story.
I was recently in an air plane, writing code, when I realised that I needed to add a couple of NuGet packages to my code base. I was on one of those less-travelled flights in Europe, on board an Embraer E190, and as is usually the case on those 1½-hour flights, there was no WiFi.
Adding a NuGet package typically requires that you're online so that the tools can query the relevant NuGet repository. You'll need to download the package, so if you're offline, you're just out of luck, right?
Fortunately, I'd previously used the packages I needed in other projects, on the same laptop. While I'm no fan of package restore, I know that the local NuGet tools cache packages somewhere on the local machine.
So, perhaps I could entice the tools to reuse a cached package...
First, I simply tried adding a package that I needed:
$ dotnet add package unquote Determining projects to restore... Writing C:\Users\mark\AppData\Local\Temp\tmpF3C.tmp info : X.509 certificate chain validation will use the default trust store selected by .NET. info : Adding PackageReference for package 'unquote' into project '[redacted]'. error: Unable to load the service index for source https://api.nuget.org/v3/index.json. error: No such host is known. (api.nuget.org:443) error: No such host is known.
Fine plan, but no success.
Clearly the dotnet tool was trying to access api.nuget.org, which, obviously, couldn't be reached because my laptop was in flight mode. It occurred to me, though, that the reason that the tool was querying api.nuget.org was that it wanted to see which version of the package was the most recent. After all, I hadn't specified a version.
What if I were to specify a version? Would the tool use the cached version of the package?
That seemed worth a try, but which versions did I already have on my laptop?
I don't go around remembering which version numbers I've used of various NuGet packages, but I expected the NuGet tooling to have that information available, somewhere.
But where? Keep in mind that I was offline, so couldn't easily look this up.
On the other hand, I knew that these days, most Windows applications keep data of that kind somewhere in AppData, so I started spelunking around there, looking for something that might be promising.
After looking around a bit, I found a subdirectory named AppData\Local\NuGet\v3-cache. This directory contained a handful of subdirectories obviously named with GUIDs. Each of these contained a multitude of .dat files. The names of those files, however, looked promising:
list_antlr_index.dat list_autofac.dat list_autofac.extensions.dependencyinjection.dat list_autofixture.automoq.dat list_autofixture.automoq_index.dat list_autofixture.automoq_range_2.0.0-3.6.7.dat list_autofixture.automoq_range_3.30.3-3.50.5.dat list_autofixture.automoq_range_3.50.6-4.17.0.dat list_autofixture.automoq_range_3.6.8-3.30.2.dat list_autofixture.dat ...
and so on.
These names were clearly(?) named list_[package-name].dat or list_[package-name]_index.dat, so I started looking around for one named after the package I was looking for (Unquote).
Often, both files are present, which was also the case for Unquote.
$ ls list_unquote* -l -rw-r--r-- 1 mark 197609 348 Oct 1 18:38 list_unquote.dat -rw-r--r-- 1 mark 197609 42167 Sep 23 21:29 list_unquote_index.dat
As you can tell, list_unquote_index.dat is much larger than list_unquote.dat. Since I didn't know what the format of these files were, I decided to look at the smallest one first. It had this content:
{
"versions": [
"1.3.0",
"2.0.0",
"2.0.1",
"2.0.2",
"2.0.3",
"2.1.0",
"2.1.1",
"2.2.0",
"2.2.1",
"2.2.2",
"3.0.0",
"3.1.0",
"3.1.1",
"3.1.2",
"3.2.0",
"4.0.0",
"5.0.0",
"6.0.0-rc.1",
"6.0.0-rc.2",
"6.0.0-rc.3",
"6.0.0",
"6.1.0"
]
}
A list of versions. Sterling. It looked as though version 6.1.0 was the most recent one on my machine, so I tried to add that one to my code base:
$ dotnet add package unquote --version 6.1.0 Determining projects to restore... Writing C:\Users\mark\AppData\Local\Temp\tmp815D.tmp info : X.509 certificate chain validation will use the default trust store selected by .NET. info : Adding PackageReference for package 'unquote' into project '[redacted]'. info : Restoring packages for [redacted]... info : Package 'unquote' is compatible with all the specified frameworks in project '[redacted]'. info : PackageReference for package 'unquote' version '6.1.0' added to file '[redacted]'. info : Generating MSBuild file [redacted]. info : Writing assets file to disk. Path: [redacted] log : Restored [redacted] (in 397 ms).
Jolly good! That worked.
This way I managed to install all the NuGet packages I needed. This was fortunate, because I had so little time to transfer to my connecting flight that I never got to open the laptop before I was airborne again - in another E190 without WiFi, and another session of offline programming.
Functors as invariant functors
A most likely useless set of invariant functors that nonetheless exist.
This article is part of a series of articles about invariant functors. An invariant functor is a functor that is neither covariant nor contravariant. See the series introduction for more details.
It turns out that all functors are also invariant functors.
Is this useful? Let me be honest and say that if it is, I'm not aware of it. Thus, if you're interested in practical applications, you can stop reading here. This article contains nothing of practical use - as far as I can tell.
Because it's there #
Why describe something of no practical use?
Why do some people climb Mount Everest? Because it's there, or for other irrational reasons. Which is fine. I've no personal goals that involve climbing mountains, but I happily engage in other irrational and subjective activities.
One of them, apparently, is to write articles of software constructs of no practical use, because it's there.
All functors are also invariant functors, even if that's of no practical use. That's just the way it is. This article explains how, and shows a few (useless) examples.
I'll start with a few Haskell examples and then move on to showing the equivalent examples in C#. If you're unfamiliar with Haskell, you can skip that section.
Haskell package #
For Haskell you can find an existing definition and implementations in the invariant package. It already makes most common functors Invariant instances, including [] (list), Maybe, and Either. Here's an example of using invmap with a small list:
ghci> invmap secondsToNominalDiffTime nominalDiffTimeToSeconds [0.1, 60] [0.1s,60s]
Here I'm using the time package to convert fixed-point decimals into NominalDiffTime values.
How is this different from normal functor mapping with fmap? In observable behaviour, it's not:
ghci> fmap secondsToNominalDiffTime [0.1, 60] [0.1s,60s]
When invariantly mapping a functor, only the covariant mapping function a -> b is used. Here, that's secondsToNominalDiffTime. The contravariant mapping function b -> a (nominalDiffTimeToSeconds) is simply ignored.
While the invariant package already defines certain common functors as Invariant instances, every Functor instance can be converted to an Invariant instance. There are two ways to do that: invmapFunctor and WrappedFunctor.
In order to demonstrate, we need a custom Functor instance. This one should do:
data Pair a = Pair (a, a) deriving (Eq, Show, Functor)
If you just want to perform an ad-hoc invariant mapping, you can use invmapFunctor:
ghci> invmapFunctor secondsToNominalDiffTime nominalDiffTimeToSeconds $ Pair (0.1, 60) Pair (0.1s,60s)
I can't think of any reason to do this, but it's possible.
WrappedFunctor is perhaps marginally more relevant. If you run into a function that takes an Invariant argument, you can convert any Functor to an Invariant instance by wrapping it in WrappedFunctor:
ghci> invmap secondsToNominalDiffTime nominalDiffTimeToSeconds $ WrapFunctor $ Pair (0.1, 60)
WrapFunctor {unwrapFunctor = Pair (0.1s,60s)}
A realistic, useful example still escapes me, but there it is.
Pair as an invariant functor in C# #
What would the above Haskell example look like in C#? First, we're going to need a Pair data structure:
public sealed class Pair<T> { public Pair(T x, T y) { X = x; Y = y; } public T X { get; } public T Y { get; } // More members follow...
Making Pair<T> a functor is so easy that Haskell can do it automatically with the DeriveFunctor extension. In C# you must explicitly write the function:
public Pair<T1> Select<T1>(Func<T, T1> selector) { return new Pair<T1>(selector(X), selector(Y)); }
An example equivalent to the above fmap example might be this, here expressed as a unit test:
[Fact] public void FunctorExample() { Pair<long> sut = new Pair<long>( TimeSpan.TicksPerSecond / 10, TimeSpan.TicksPerSecond * 60); Pair<TimeSpan> actual = sut.Select(ticks => new TimeSpan(ticks)); Assert.Equal( new Pair<TimeSpan>( TimeSpan.FromSeconds(.1), TimeSpan.FromSeconds(60)), actual); }
You can trivially make Pair<T> an invariant functor by giving it a function equivalent to invmap. As I outlined in the introduction it's possible to add an InvMap method to the class, but it might be more idiomatic to instead add a Select overload:
public Pair<T1> Select<T1>(Func<T, T1> tToT1, Func<T1, T> t1ToT) { return Select(tToT1); }
Notice that this overload simply ignores the t1ToT argument and delegates to the normal Select overload. That's consistent with the Haskell package. This unit test shows an examples:
[Fact] public void InvariantFunctorExample() { Pair<long> sut = new Pair<long>( TimeSpan.TicksPerSecond / 10, TimeSpan.TicksPerSecond * 60); Pair<TimeSpan> actual = sut.Select(ticks => new TimeSpan(ticks), ts => ts.Ticks); Assert.Equal( new Pair<TimeSpan>( TimeSpan.FromSeconds(.1), TimeSpan.FromSeconds(60)), actual); }
I can't think of a reason to do this in C#. In Haskell, at least, you have enough power of abstraction to describe something as simply an Invariant functor, and then let client code decide whether to use Maybe, [], Endo, or a custom type like Pair. You can't do that in C#, so the abstraction is even less useful here.
Conclusion #
All functors are invariant functors. You simply use the normal functor mapping function (fmap in Haskell, map in many other languages, Select in C#). This enables you to add an invariant mapping (invmap) that only uses the covariant argument (a -> b) and ignores the contravariant argument (b -> a).
Invariant functors are, however, not particularly useful, so neither is this result. Still, it's there, so deserves a mention. The situation is similar for the next article.
Error-accumulating composable assertions in C#
Perhaps the list monoid is all you need for non-short-circuiting assertions.
This article is the second instalment in a small articles series about applicative assertions. It explores a way to compose assertions in such a way that failure messages accumulate rather than short-circuit. It assumes that you've read the article series introduction and the previous article.
Unsurprisingly, the previous article showed that you can use an applicative functor to create composable assertions that don't short-circuit. It also concluded that, in C# at least, the API is awkward.
This article explores a simpler API.
A clue left by the proof of concept #
The previous article's proof of concept left a clue suggesting a simpler API. Consider, again, how the rather horrible RunAssertions method decides whether or not to throw an exception:
string errors = composition.Match( onFailure: f => string.Join(Environment.NewLine, f), onSuccess: _ => string.Empty); if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(errors)) throw new Exception(errors);
Even though Validated<F, S> is a sum type, the RunAssertions method declines to take advantage of that. Instead, it reduces composition to a simple type: A string. It then decides to throw an exception if the errors value is not null or empty.
This suggests that using a sum type may not be necessary to distinguish between the success and the failure case. Rather, an empty error string is all it takes to indicate success.
Non-empty errors #
The proof-of-concept assertion type is currently defined as Validated with a particular combination of type arguments: Validated<IReadOnlyCollection<string>, Unit>. Consider, again, this Match expression:
string errors = composition.Match( onFailure: f => string.Join(Environment.NewLine, f), onSuccess: _ => string.Empty);
Does an empty string unambiguously indicate success? Or is it possible to arrive at an empty string even if composition actually represents a failure case?
You can arrive at an empty string from a failure case if the collection of error messages is empty. Consider the type argument that takes the place of the F generic type: IReadOnlyCollection<string>. A collection of this type can be empty, which would also cause the above Match to produce an empty string.
Even so, the proof-of-concept works in practice. The reason it works is that failure cases will never have empty assertion messages. We know this because (in the proof-of-concept code) only two functions produce assertions, and they each populate the error message collection with a string. You may want to revisit the AssertTrue and AssertEqual functions in the previous article to convince yourself that this is true.
This is a good example of knowledge that 'we' as developers know, but the code currently doesn't capture. Having to deal with such knowledge taxes your working memory, so why not encapsulate such information in the type itself?
How do you encapsulate the knowledge that a collection is never empty? Introduce a NotEmptyCollection collection. I'll reuse the class from the article Semigroups accumulate and add a Concat instance method:
public NotEmptyCollection<T> Concat(NotEmptyCollection<T> other) { return new NotEmptyCollection<T>(Head, Tail.Concat(other).ToArray()); }
Since the two assertion-producing functions both supply an error message in the failure case, it's trivial to change them to return Validated<NotEmptyCollection<string>, Unit> - just change the types used:
public static Validated<NotEmptyCollection<string>, Unit> AssertTrue( this bool condition, string message) { return condition ? Succeed<NotEmptyCollection<string>, Unit>(Unit.Value) : Fail<NotEmptyCollection<string>, Unit>(new NotEmptyCollection<string>(message)); } public static Validated<NotEmptyCollection<string>, Unit> AssertEqual<T>( T expected, T actual) { return Equals(expected, actual) ? Succeed<NotEmptyCollection<string>, Unit>(Unit.Value) : Fail<NotEmptyCollection<string>, Unit>( new NotEmptyCollection<string>($"Expected {expected}, but got {actual}.")); }
This change guarantees that the RunAssertions method only produces an empty errors string in success cases.
Error collection isomorphism #
Assertions are still defined by the Validated sum type, but the success case carries no information: Validated<NotEmptyCollection<T>, Unit>, and the failure case is always guaranteed to contain at least one error message.
This suggests that a simpler representation is possible: One that uses a normal collection of errors, and where an empty collection indicates an absence of errors:
public class Asserted<T> { public Asserted() : this(Array.Empty<T>()) { } public Asserted(T error) : this(new[] { error }) { } public Asserted(IReadOnlyCollection<T> errors) { Errors = errors; } public Asserted<T> And(Asserted<T> other) { if (other is null) throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(other)); return new Asserted<T>(Errors.Concat(other.Errors).ToList()); } public IReadOnlyCollection<T> Errors { get; } }
The Asserted<T> class is scarcely more than a glorified wrapper around a normal collection, but it's isomorphic to Validated<NotEmptyCollection<T>, Unit>, which the following two functions prove:
public static Asserted<T> FromValidated<T>(this Validated<NotEmptyCollection<T>, Unit> v) { return v.Match( failures => new Asserted<T>(failures), _ => new Asserted<T>()); } public static Validated<NotEmptyCollection<T>, Unit> ToValidated<T>(this Asserted<T> a) { if (a.Errors.Any()) { var errors = new NotEmptyCollection<T>( a.Errors.First(), a.Errors.Skip(1).ToArray()); return Validated.Fail<NotEmptyCollection<T>, Unit>(errors); } else return Validated.Succeed<NotEmptyCollection<T>, Unit>(Unit.Value); }
You can translate back and forth between Validated<NotEmptyCollection<T>, Unit> and Asserted<T> without loss of information.
A collection, however, gives rise to a monoid, which suggests a much simpler way to compose assertions than using an applicative functor.
Asserted truth #
You can now rewrite the assertion-producing functions to return Asserted<string> instead of Validated<NotEmptyCollection<string>, Unit>.
public static Asserted<string> True(bool condition, string message) { return condition ? new Asserted<string>() : new Asserted<string>(message); }
This Asserted.True function returns no error messages when condition is true, but a collection with the single element message when it's false.
You can use it in a unit test like this:
var assertResponse = Asserted.True( deleteResp.IsSuccessStatusCode, $"Actual status code: {deleteResp.StatusCode}.");
You'll see how assertResponse composes with another assertion later in this article. The example continues from the previous article. It's the same test from the same code base.
Asserted equality #
You can also rewrite the other assertion-producing function in the same way:
public static Asserted<string> Equal(object expected, object actual) { if (Equals(expected, actual)) return new Asserted<string>(); return new Asserted<string>($"Expected {expected}, but got {actual}."); }
Again, when the assertion passes, it returns no errors; otherwise, it returns a collection with a single error message.
Using it may look like this:
var getResp = await api.CreateClient().GetAsync(address); var assertState = Asserted.Equal(HttpStatusCode.NotFound, getResp.StatusCode);
At this point, each of the assertions are objects that represent a verification step. By themselves, they neither pass nor fail the test. You have to execute them to reach a verdict.
Evaluating assertions #
The above code listing of the Asserted<T> class already shows how to combine two Asserted<T> objects into one. The And instance method is a binary operation that, together with the parameterless constructor, makes Asserted<T> a monoid.
Once you've combined all assertions into a single Asserted<T> object, you need to Run it to produce a test outcome:
public static void Run(this Asserted<string> assertions) { if (assertions?.Errors.Any() ?? false) { var messages = string.Join(Environment.NewLine, assertions.Errors); throw new Exception(messages); } }
If there are no errors, Run does nothing; otherwise it combines all the error messages together and throws an exception. As was also the case in the previous article, I've allowed myself a few proof-of-concept shortcuts. The framework design guidelines admonishes against throwing System.Exception. It might be more appropriate to introduce a new Exception type that also allows enumerating the error messages.
The entire assertion phase of the test looks like this:
var assertResponse = Asserted.True( deleteResp.IsSuccessStatusCode, $"Actual status code: {deleteResp.StatusCode}."); var getResp = await api.CreateClient().GetAsync(address); var assertState = Asserted.Equal(HttpStatusCode.NotFound, getResp.StatusCode); assertResponse.And(assertState).Run();
You can see the entire test in the previous article. Notice how the two assertion objects are first combined into one with the And binary operation. The result is a single Asserted<string> object on which you can call Run.
Like the previous proof of concept, this assertion passes and fails in the same way. It's possible to compose assertions and collect error messages, instead of short-circuiting on the first failure, even without an applicative functor.
Method chaining #
If you don't like to come up with variable names just to make assertions, it's also possible to use the Asserted API's fluent interface:
var getResp = await api.CreateClient().GetAsync(address); Asserted .True( deleteResp.IsSuccessStatusCode, $"Actual status code: {deleteResp.StatusCode}.") .And(Asserted.Equal(HttpStatusCode.NotFound, getResp.StatusCode)) .Run();
This isn't necessarily better, but it's an option.
Conclusion #
While it's possible to design non-short-circuiting composable assertions using an applicative functor, it looks as though a simpler solution might solve the same problem. Collect error messages. If none were collected, interpret that as a success.
As I wrote in the introduction article, however, this may not be the last word. Some assertions return values that can be used for other assertions. That's a scenario that I have not yet investigated in this light, and it may change the conclusion. If so, I'll add more articles to this small article series. As I'm writing this, though, I have no such plans.
Did I just, in a roundabout way, write that more research is needed?
Comments
I think NUnit's Assert.Multiple is worth mentioning in this series. It does not require any complicated APIs, just wrap your existing test with multiple asserts into a delegate.
Pavel, thank you for writing. I'm aware of both that API and similar ones for other testing frameworks. As is usually the case, there are trade-offs to consider. I'm currently working on some material that may turn into another article about that.
A new article is now available: Built-in alternatives to applicative assertions.
When do tests fail?
Optimise for the common scenario.
Unit tests occasionally fail. When does that happen? How often? What triggers it? What information is important when tests fail?
Regularly I encounter the viewpoint that it should be easy to understand the purpose of a test when it fails. Some people consider test names important, a topic that I've previously discussed. Recently I discussed the Assertion Roulette test smell on Twitter, and again I learned some surprising things about what people value in unit tests.
The importance of clear assertion messages #
The Assertion Roulette test smell is often simplified to degeneracy, but it really describes situations where it may be a problem if you can't tell which of several assertions actually caused a test to fail.
Josh McKinney gave a more detailed example than Gerard Meszaros does in the book:
"Background. In a legacy product, we saw some tests start failing intermittently. They weren’t just flakey, but also failed without providing enough info to fix. One of things which caused time to fix to increase was multiple ways of a single test to fail."
He goes on:
"I.e. if you fix the first assertion and you know there still could be flakiness, or long cycle times to see the failure. Multiple assertions makes any test problem worse. In an ideal state, they are fine, but every assertion doubles the amount of failures a test catches."
and concludes:
"the other main way (unrelated) was things like:
assertTrue(someListResult.isRmpty())
Which tells you what failed, but nothing about how.
But the following is worse. You must run the test twice to fix:
assertFalse(someList.isEmpty());
assertEqual(expected, list.get(0));"
The final point is due to the short-circuiting nature of most assertion libraries. That, however, is a solvable problem.
I find the above a compelling example of why Assertion Roulette may be problematic.
It did give me pause, though. How common is this scenario?
Out of the blue #
The situation described by Josh McKinney comes with more than a single warning flag. I hope that it's okay to point some of them out. I didn't get the impression from my interaction with Josh McKinney that he considered the situation ideal in any way.
First, of course, there's the lack of information about the problem. Here, that's a real problem. As I understand it, it makes it harder to reproduce the problem in a development environment.
Next, there's long cycle times, which I interpret as significant time may pass from when you attempt a fix until you can actually observe whether or not it worked. Josh McKinney doesn't say how long, but I wouldn't surprised if it was measured in days. At least, if the cycle time is measured in days, I can see how this is a problem.
Finally, there's the observation that "some tests start failing intermittently". This was the remark that caught my attention. How often does that happen?
Tests shouldn't do that. Tests should be deterministic. If they're not, you should work to eradicate non-determinism in tests.
I'll be the first to admit that that I also write non-deterministic tests. Not by design, but because I make mistakes. I've written many Erratic Tests in my career, and I've documented a few of them here:
- Waiting to happen
- Waiting to never happen
- Fortunately, I don't squash my commits
- Make pre-conditions explicit in Property-Based Tests
While it can happen, it shouldn't be the norm. When it nonetheless happens, eradicating that source of non-determinism should be top priority. Pull the andon cord.
When tests fail #
Ideally, tests should rarely fail. As examined above, you may have Erratic Tests in your test suite, and if you do, these tests will occasionally (or often) fail. As Martin Fowler writes, this is a problem and you should do something about it. He also outlines strategies for it.
Once you've eradicated non-determinism in unit tests, then when do tests fail?
I can think of a couple of situations.
Tests routinely fail as part of the red-green-refactor cycle. This is by design. If no test is failing in the red phase, you probably made a mistake (which also regularly happens to me), or you may not really be doing test-driven development (TDD).
Another situation that may cause a test to fail is if you changed some code and triggered a regression test.
In both cases, tests don't just fail out of the blue. They fail as an immediate consequence of something you did.
Optimise for the common scenario #
In both cases you're (hopefully) in a tight feedback loop. If you're in a tight feedback loop, then how important is the assertion message really? How important is the test name?
You work on the code base, make some changes, run the tests. If one or more tests fail, it's correlated to the change you just made. You should have a good idea of what went wrong. Are code forensics and elaborate documentation really necessary to understand a test that failed because you just did something a few minutes before?
The reason I don't care much about test names or whether there's one or more assertion in a unit test is exactly that: When tests fail, it's usually because of something I just did. I don't need diagnostics tools to find the root cause. The root cause is the change that I just made.
That's my common scenario, and I try to optimise my processes for the common scenarios.
Fast feedback #
There's an implied way of working that affects such attitudes. Since I learned about TDD in 2003 I've always relished the fast feedback I get from a test suite. Since I tried continuous deployment around 2014, I consider it central to modern software engineering (and Accelerate strongly suggests so, too).
The modus operandi I outline above is one of fast feedback. If you're sitting on a feature branch for weeks before integrating into master, or if you can only deploy two times a year, this influences what works and what doesn't.
Both Modern Software Engineering and Accelerate make a strong case that short feedback cycles are pivotal for successful software development organisations.
I also understand that that's not the reality for everyone. When faced with long cycle times, a multitude of Erratic Tests, a legacy code base, and so on, other things become important. In those circumstances, tests may fail for different reasons.
When you work with TDD, continuous integration (CI), and continuous deployment (CD), then when do tests fail? They fail because you made them fail, only minutes earlier. Fix your code and move forward.
Conclusion #
When discussing test names and assertion messages, I've been surprised by the emphasis some people put on what I consider to be of secondary importance. I think the explanation is that circumstances differ.
With TDD and CI/CD you mostly look at a unit test when you write it, or if some regression test fails because you changed some code (perhaps in response to a test you just wrote). Your test suite may have hundreds or thousands of tests. Most of these pass every time you run the test suite. That's the normal state of affairs.
In other circumstances, you may have Erratic Tests that fail unpredictably. You should make it a priority to stop that, but as part of that process, you may need good assertion messages and good test names.
Different circumstances call for different reactions, so what works well in one situation may be a liability in other situations. I hope that this article has shed a little light on the forces you may want to consider.
GitHub Copilot preliminary experience report
Based on a few months of use.
I've been evaluating GitHub Copilot since August 2022. Perhaps it's time to collect my thoughts so far.
In short, it's surprisingly good, but also gets a lot of things wrong. It does seem helpful to the experienced programmer, but I don't see it replacing all programmers yet.
Not only for boilerplate code #
I was initially doubtful. I'd seen some demos where Copilot created fifteen to twenty lines of code to, say, make a REST API request. These examples mostly struck me as auto-generation of something that ought to be a proper abstraction: A method in a reusable library.
In general I don't think that typing is a productivity bottleneck, and I'm sceptical of productivity tools, and particularly code generators. The more code a code base contains, the more code there is to read. Accelerating code production doesn't strike me as a goal in itself.
On the other hand, I'm past fifty and aware that in my age, one often tends to resist new ideas. Perhaps the above justifications are nothing but motivated reasoning. I decided to install the plug-ins and go about my business to see what would happen.
It has surprised and delighted me more than once. It's not only for boilerplate code. Here's a recent example.
I was doing an exercise in F# and wrote this type definition:
type Instruction = Enqueue of int | Dequeue
I wanted to write a property-based test with this type, and since I was using Hedgehog I needed a generator for the type. While FsCheck can automatically generate values of custom discriminated unions, Hedgehog has a more explicit-is-better-than-implicit design philosophy. In other words, if there's a way to make Hedgehog automatically generate values of a type like the above Instruction, it has so far escaped me.
So I started typing let private genInstruction = after which Copilot suggested the following:
let private genInstruction = Gen.frequency [ 1, Gen.constant Dequeue 1, Gen.int32 (Range.constant 0 10_000) |> Gen.map Enqueue ]
I was, frankly, stunned. While I do understand that Copilot doesn't actually understand the code it suggests, Hedgehog is sufficiently esoteric that I didn't expect Copilot to have enough training data to enable it to make a useful contribution in this niche. I was wrong. I've repeatedly seen Copilot make suggestions to my F# and Haskell code. It's not just for C#, JavaScript, or python code.
The above suggestion was, to be clear, absolutely appropriate and compiled right away. The only detail I decided to change was the Range, which I decided to change to Range.linear. That's not, however, a significant change.
Perhaps you're not impressed by three lines of auto-generated code. How much of a productivity improvement is that? Quite a bit, in my case.
It wouldn't have taken me long to type those three lines of code, but as I already mentioned, typing isn't a bottleneck. On the other hand, looking up an unfamiliar API can take some time. The Programmer's Brain discusses this kind of problem and suggests exercises to address it. Does Copilot offer a shortcut?
While I couldn't remember the details of Hedgehog's API, once I saw the suggestion, I recognised Gen.frequency, so I understood it as an appropriate code suggestion. The productivity gain, if there is one, may come from saving you the effort of looking up unfamiliar APIs, rather than saving you some keystrokes.
In this example, I already knew of the Gen.frequency function - I just couldn't recall the exact name and type. This enabled me to evaluate Copilot's suggestion and deem it correct. If I hadn't known that API already, how could I have known whether to trust Copilot?
Detectably wrong suggestions #
As amazing as Copilot can be, it's hardly faultless. It makes many erroneous suggestions. Sometimes the suggestion is obviously wrong. If you accept it, it doesn't compile. Sometimes, the compilation error is only a little edit from being correct, but at least in such situations you'll be explicitly aware that the suggestion couldn't be used verbatim.
Other suggestions are wrong, but less conspicuously so. Here's an example.
I was recently subjecting the code base that accompanies Code That Fits in Your Head to the mutation testing tool Stryker. Since it did point out a few possible mutations, I decided to add a few tests. One was of a wrapper class called TimeOfDay. Because of static code analysis rules, it came with conversions to and from TimeSpan, but these methods weren't covered by any tests.
In order to remedy that situation, I started writing an FsCheck property and came as far as:
[Property] public void ConversionsRoundTrip(TimeSpan timeSpan)
At that point Copilot suggested the following, which I accepted:
[Property] public void ConversionsRoundTrip(TimeSpan timeSpan) { var timeOfDay = new TimeOfDay(timeSpan); var actual = (TimeSpan)timeOfDay; Assert.Equal(timeSpan, actual); }
Looks good, doesn't it? Again, I was impressed. It compiled, and it even looks as though Copilot had picked up one of my naming conventions: naming variables by role, in this case actual.
While I tend to be on guard, I immediately ran the test suite instead of thinking it through. It failed. Keep in mind that this is a characterisation test, so it was supposed to pass.
The TimeOfDay constructor reveals why:
public TimeOfDay(TimeSpan durationSinceMidnight) { if (durationSinceMidnight < TimeSpan.Zero || TimeSpan.FromHours(24) < durationSinceMidnight) throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException( nameof(durationSinceMidnight), "Please supply a TimeSpan between 0 and 24 hours."); this.durationSinceMidnight = durationSinceMidnight; }
While FsCheck knows how to generate TimeSpan values, it'll generate arbitrary durations, including negative values and spans much longer than 24 hours. That explains why the test fails.
Granted, this is hardly a searing indictment against Copilot. After all, I could have made this mistake myself.
Still, that prompted me to look for more issues with the code that Copilot had suggested. Another problem with the code is that it tests the wrong API. The suggested test tries to round-trip via the TimeOfDay class' explicit cast operators, which were already covered by tests. Well, I might eventually have discovered that, too. Keep in mind that I was adding this test to improve the code base's Stryker score. After running the tool again, I would probably eventually have discovered that the score didn't improve. It takes Stryker around 25 minutes to test this code base, though, so it wouldn't have been rapid feedback.
Since, however, I examined the code with a critical eye, I noticed this by myself. This would clearly require changing the test code as well.
In the end, I wrote this test:
[Property] public void ConversionsRoundTrip(TimeSpan timeSpan) { var expected = ScaleToTimeOfDay(timeSpan); var sut = TimeOfDay.ToTimeOfDay(expected); var actual = TimeOfDay.ToTimeSpan(sut); Assert.Equal(expected, actual); } private static TimeSpan ScaleToTimeOfDay(TimeSpan timeSpan) { // Convert an arbitrary TimeSpan to a 24-hour TimeSpan. // The data structure that underlies TimeSpan is a 64-bit integer, // so first we need to identify the range of possible TimeSpan // values. It might be easier to understand to calculate // TimeSpan.MaxValue - TimeSpan.MinValue, but that underflows. // Instead, the number of possible 64-bit integer values is the same // as the number of possible unsigned 64-bit integer values. var range = ulong.MaxValue; var domain = TimeSpan.FromHours(24).Ticks; var scale = (ulong)domain / range; var expected = timeSpan * scale; return expected; }
In this case, Copilot didn't improve my productivity. It may actually have slowed me down a bit.
This time, it wasn't too difficult to spot issues with the suggested code. What if the problems are more subtle?
Errors that are difficult to detect #
How do bugs appear? We write them, thinking that our code is going to do one thing, while the compiler decides otherwise. Even when we actively engage with the code, we may be looking at a bug and still fail to see it.
Why should we trust Copilot to produce bug-free code?
Here's another example. I was going through the Range kata in F# and made my Endpoint discriminated union a functor:
type Endpoint<'a> = Open of 'a | Closed of 'a module Endpoint = let map f = function | Open x -> Open (f x) | Closed x -> Closed (f x)
Making a type a functor is such a well-understood process that Haskell can automate it. I knew how to write the above map function as well, so I wrote it without testing it.
After I'd written the map function, I decided to add tests of the two functor laws. Not because I doubted the implementation, but because I might need that as example code later.
Copilot suggested this test after I named it:
open Xunit open Hedgehog [<Fact>] let ``First functor law`` () = Property.check <| property { let! x = Gen.int32 (Range.linearBounded ()) let f = (fun x -> x + 1) let g = (fun x -> x * 2) let actual = Endpoint.map f (Endpoint.map g (Open x)) let expected = Endpoint.map (f >> g) (Open x) Assert.Equal(expected, actual) }
It compiles. It also fails.
What's wrong with it?
If you know the functor laws by heart, you'll be able to spot that this is clearly not the first functor law. On the other hand, it looks convincingly like the second functor law. Should I just change the name and move on?
I can't, though, since the test fails. Could there be a bug in my map function, after all?
No, there's an error in the test. I invite you to spot it.
In terms of keystrokes, it's easy to fix the problem:
open Xunit open Hedgehog [<Fact>] let ``First functor law`` () = Property.check <| property { let! x = Gen.int32 (Range.linearBounded ()) let f = (fun x -> x + 1) let g = (fun x -> x * 2) let actual = Endpoint.map f (Endpoint.map g (Open x)) let expected = Endpoint.map (f << g) (Open x) Assert.Equal(expected, actual) }
Spot the edit. I bet it'll take you longer to find it than it took me to type it.
The test now passes, but for one who has spent less time worrying over functor laws than I have, troubleshooting this could have taken a long time.
These almost-right suggestions from Copilot both worry me and give me hope.
Copilot for experienced programmers #
When a new technology like Copilot appears, it's natural to speculate on the consequences. Does this mean that programmers will lose their jobs?
This is just a preliminary evaluation after a few months, so I could be wrong, but I think we programmers are safe. If you're experienced, you'll be able to tell most of Copilot's hits from its misses. Perhaps you'll get a productivity improvement out of, but it could also slow you down.
The tool is likely to improve over time, so I'm hopeful that this could become a net productivity gain. Still, with this high an error rate, I'm not too worried yet.
The Pragmatic Programmer describes a programming style named Programming by Coincidence. People who develop software this way have only a partial understanding of the code they write.
"Fred doesn't know why the code is failing because he didn't know why it worked in the first place."
I've encountered my fair share of these people. When editing code, they make small adjustments and do cursory manual testing until 'it looks like it works'. If they have to start a new feature or are otherwise faced with a metaphorical blank page, they'll copy some code from somewhere else and use that as a starting point.
You'd think that Copilot could enhance the productivity of such people, but I'm not sure. It might actually slow them down. These people don't fully understand the code they themselves 'write', so why should we expect them to understand the code that Copilot suggests?
If faced with a Copilot suggestion that 'almost works', will they be able to spot if it's a genuinely good suggestion, or whether it's off, like I've described above? If the Copilot code doesn't work, how much time will they waste thrashing?
Conclusion #
GitHub Copilot has the potential to be a revolutionary technology, but it's not, yet. So far, I'm not too worried. It's an assistant, like a pairing partner, but it's up to you to evaluate whether the code that Copilot suggests is useful, correct, and safe. How can you do that unless you already know what you're doing?
If you don't have the qualifications to evaluate the suggested code, I fail to see how it's going to help you. Granted, it does have potential to help you move on in less time that you would otherwise have spent. In this article, I showed one example where I would have had to spend significant time looking up API documentation. Instead, Copilot suggested the correct code to use.
Pulling in the other direction are the many false positives. Copilot makes many suggestions, and many of them are poor. The ones that are recognisably bad are unlikely to slow you down. I'm more concerned with those that are subtly wrong. They have the potential to waste much time.
Which of these forces are strongest? The potential for wasting time is infinite, while the maximum productivity gain you can achieve is 100 percent. That's an asymmetric distribution. There's a long tail of time wasters, but there's no equivalent long tail of improvement.
I'm not, however, trying to be pessimistic. I expect to keep Copilot around for the time being. It could very well be here to stay. Used correctly, it seems useful.
Is it going to replace programmers? Hardly. Rather, it may enable poor developers to make such a mess of things that you need even more good programmers to subsequently fix things.
An initial proof of concept of applicative assertions in C#
Worthwhile? Not obviously.
This article is the first instalment in a small articles series about applicative assertions. It explores a way to compose assertions in such a way that failure messages accumulate rather than short-circuit. It assumes that you've read the article series introduction.
Assertions are typically based on throwing exceptions. As soon as one assertion fails, an exception is thrown and no further assertions are evaluated. This is normal short-circuiting behaviour of exceptions. In some cases, however, it'd be useful to keep evaluating other assertions and collect error messages.
This article series explores an intriguing idea to address such issues: Use an applicative functor to collect multiple assertion messages. I started experimenting with the idea to see where it would lead. The article series serves as a report of what I found. It is neither a recommendation nor a caution. I still find the idea interesting, but I'm not sure whether the complexity is warranted.
Example scenario #
A realistic example is often illustrative, although there's a risk that the realism carries with it some noise that detracts from the core of the matter. I'll reuse an example that I've already discussed and explained in greater detail. The code is from the code base that accompanies my book Code That Fits in Your Head.
This test has two independent assertions:
[Theory] [InlineData(884, 18, 47, "c@example.net", "Nick Klimenko", 2)] [InlineData(902, 18, 50, "emot@example.gov", "Emma Otting", 5)] public async Task DeleteReservation( int days, int hours, int minutes, string email, string name, int quantity) { using var api = new LegacyApi(); var at = DateTime.Today.AddDays(days).At(hours, minutes) .ToIso8601DateTimeString(); var dto = Create.ReservationDto(at, email, name, quantity); var postResp = await api.PostReservation(dto); Uri address = FindReservationAddress(postResp); var deleteResp = await api.CreateClient().DeleteAsync(address); Assert.True( deleteResp.IsSuccessStatusCode, $"Actual status code: {deleteResp.StatusCode}."); var getResp = await api.CreateClient().GetAsync(address); Assert.Equal(HttpStatusCode.NotFound, getResp.StatusCode); }
The test exercises the REST API to first create a reservation, then delete it, and finally check that the reservation no longer exists. Two independent postconditions must be true for the test to pass:
- The
DELETErequest must result in a status code that indicates success. - The resource must no longer exist.
It's conceivable that a bug might fail one of these without invalidating the other.
As the test is currently written, it uses xUnit.net's standard assertion library. If the Assert.True verification fails, the Assert.Equal statement isn't evaluated.
Assertions as validations #
Is it possible to evaluate the Assert.Equal postcondition even if the first assertion fails? You could use a try/catch block, but is there a more composable and elegant option? How about an applicative functor?
Since I was interested in exploring this question as a proof of concept, I decided to reuse the machinery that I'd already put in place for the article An applicative reservation validation example in C#: The Validated class and its associated functions. In a sense, you can think of an assertion as a validation of a postcondition.
This is not a resemblance I intend to carry too far. What I learn by experimenting with Validated I can apply to a more appropriately-named class like Asserted.
Neither of the two above assertions return a value; they are one-stop assertions. If they succeed, they return nothing; if they fail, they produce an error.
It's possible to model this kind of behaviour with Validated. You can model a collection of errors with, well, a collection. To keep the proof of concept simple, I decided to use a collection of strings: IReadOnlyCollection<string>. To model 'nothing' I had to add a unit type:
public sealed class Unit { private Unit() { } public readonly static Unit Value = new Unit(); }
This enabled me to define assertions as Validated<IReadOnlyCollection<string>, Unit> values: Either a collection of error messages, or nothing.
Asserting truth #
Instead of xUnit.net's Assert.True, you can now define an equivalent function:
public static Validated<IReadOnlyCollection<string>, Unit> AssertTrue( this bool condition, string message) { return condition ? Succeed<IReadOnlyCollection<string>, Unit>(Unit.Value) : Fail<IReadOnlyCollection<string>, Unit>(new[] { message }); }
It simply returns a Success value containing nothing when condition is true, and otherwise a Failure value containing the error message.
You can use it like this:
var assertResponse = Validated.AssertTrue( deleteResp.IsSuccessStatusCode, $"Actual status code: {deleteResp.StatusCode}.");
Later in the article you'll see how this assertion combines with another assertion.
Asserting equality #
Instead of xUnit.net's Assert.Equal, you can also define a function that works the same way but returns a Validated value:
public static Validated<IReadOnlyCollection<string>, Unit> AssertEqual<T>( T expected, T actual) { return Equals(expected, actual) ? Succeed<IReadOnlyCollection<string>, Unit>(Unit.Value) : Fail<IReadOnlyCollection<string>, Unit>(new[] { $"Expected {expected}, but got {actual}." }); }
The AssertEqual function first uses Equals to compare expected with actual. If the result is true, the function returns a Success value containing nothing; otherwise, it returns a Failure value containing a failure message. Since this is only a proof of concept, the failure message is useful, but minimal.
Notice that this function returns a value of the same type (Validated<IReadOnlyCollection<string>, Unit>) as AssertTrue.
You can use the function like this:
var assertState = Validated.AssertEqual(HttpStatusCode.NotFound, getResp.StatusCode);
Again, you'll see how to combine this assertion with the above assertResponse value later in this article.
Evaluating assertions #
The DeleteReservation test only has two independent assertions, so in my proof of concept, all I needed to do was to figure out a way to combine two applicative assertions into one, and then evaluate it. This rather horrible method does that:
public static void RunAssertions( Validated<IReadOnlyCollection<string>, Unit> assertion1, Validated<IReadOnlyCollection<string>, Unit> assertion2) { var f = Succeed<IReadOnlyCollection<string>, Func<Unit, Unit, Unit>>((_, __) => Unit.Value); Func<IReadOnlyCollection<string>, IReadOnlyCollection<string>, IReadOnlyCollection<string>> combine = (x, y) => x.Concat(y).ToArray(); Validated<IReadOnlyCollection<string>, Unit> composition = f .Apply(assertion1, combine) .Apply(assertion2, combine); string errors = composition.Match( onFailure: f => string.Join(Environment.NewLine, f), onSuccess: _ => string.Empty); if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(errors)) throw new Exception(errors);
C# doesn't have good language features for applicative functors the same way that F# and Haskell do, and although you can use various tricks to make the programming experience better that what is on display here, I was still doing a proof of concept. If it turns out that this approach is useful and warranted, we can introduce some of the facilities to make the API more palatable. For now, though, we're dealing with all the rough edges.
The way that applicative functors work, you typically use a 'lifted' function to combine two (or more) 'lifted' values. Here, 'lifted' means 'being inside the Validated container'.
Each of the assertions that I want to combine has the same type: Validated<IReadOnlyCollection<string>, Unit>. Notice that the S (success) generic type argument is Unit in both cases. While it seems redundant, formally I needed a 'lifted' function to combine two Unit values into a single value. This single value can (in principle) have any type I'd like it to have, but since you can't extract any information out of a Unit value, it makes sense to use the monoidal nature of unit to combine two into one.
Basically, you just ignore the Unit input values because they carry no information. Also, they're all the same value anyway, since the type is a Singleton. In its 'naked' form, the function might be implemented like this: (_, __) => Unit.Value. Due to the ceremony required by the combination of C# and applicative functors, however, this monoidal binary operation has to be 'lifted' to a Validated value. That's the f value in the RunAssertions function body.
The Validated.Apply function requires as an argument a function that combines the generic F (failure) values into one, in order to deal with the case where there's multiple failures. In this case F is IReadOnlyCollection<string>. Since declarations of Func values in C# requires explicit type declaration, that's a bit of a mouthful, but the combine function just concatenates two collections into one.
The RunAssertions method can now Apply both assertion1 and assertion2 to f, which produces a combined Validated value, composition. It then matches on the combined value to produce a string value. If there are no assertion messages, the result is the empty string; otherwise, the function combines the assertion messages with a NewLine between each. Again, this is proof-of-concept code. A more robust and flexible API (if warranted) might keep the errors around as a collection of strongly typed Value Objects.
Finally, if the resulting errors string is not null or empty, the RunAssertions method throws an exception with the combined error message(s). Here I once more invoked my proof-of-concept privilege to throw an Exception, even though the framework design guidelines admonishes against doing so.
Ultimately, then, the assert phase of the test looks like this:
var assertResponse = Validated.AssertTrue( deleteResp.IsSuccessStatusCode, $"Actual status code: {deleteResp.StatusCode}."); var getResp = await api.CreateClient().GetAsync(address); var assertState = Validated.AssertEqual(HttpStatusCode.NotFound, getResp.StatusCode); Validated.RunAssertions(assertResponse, assertState);
The rest of the test hasn't changed.
Outcomes #
Running the test with the applicative assertions passes, as expected. In order to verify that it works as it's supposed to, I tried to sabotage the System Under Test (SUT) in various ways. First, I made the Delete method that handles DELETE requests a no-op, while still returning 200 OK. As you'd expect, the result is a test failure with this message:
Message: System.Exception : Expected NotFound, but got OK.
This is the assertion that verifies that getResp.StatusCode is 404 Not Found. It fails because the sabotaged Delete method doesn't delete the reservation.
Then I further sabotaged the SUT to also return an incorrect status code (400 Bad Request), which produced this failure message:
Message: System.Exception : Actual status code: BadRequest. Expected NotFound, but got OK.
Notice that the message contains information about both failure conditions.
Finally, I re-enabled the correct behaviour (deleting the reservation from the data store) while still returning 400 Bad Request:
Message: System.Exception : Actual status code: BadRequest.
As desired, the assertions collect all relevant failure messages.
Conclusion #
Not surprisingly, it's possible to design a composable assertion API that collects multiple failure messages using an applicative functor. Anyone who knows how applicative validation works would have been able to predict that outcome. That's not what the above proof of concept was about. What I wanted to see was rather how it would play out in a realistic scenario, and whether using an applicative functor is warranted.
Applicative functors don't gel well with C#, so unsurprisingly the API is awkward. It's likely possible to smooth much of the friction, but without good language support and syntactic sugar, it's unlikely to become idiomatic C#.
Rather than taking the edge off the unwieldy API, the implementation of RunAssertions suggests another alternative.
Decouple to delete
Don't try to predict the future.
Do you know why it's called spaghetti code? It's a palatable metaphor. You may start with a single spaghetto, but usually, as you wind your fork around it, the whole dish follows along. Unless you're careful, eating spaghetti can be a mess.

Spaghetti code is tangled and everything is directly or transitively connected to everything else. As you try to edit the code, every change you make affects other code. Fix one thing and another thing breaks, cascading through the code base.
I was recently reading Clean Architecture, and as Robert C. Martin was explaining the Dependency Inversion Principle for the umpteenth time, my brain made a new connection. To be clear: Connecting (coupling) code is bad, but connecting ideas is good.
What a tangled web we weave #
It's impractical to write code that depends on nothing else. Most code will call other code, which again calls other code. It behoves us, though, to be careful that the web of dependencies don't get too tangled.
Imagine a code base where the dependency graph looks like this:
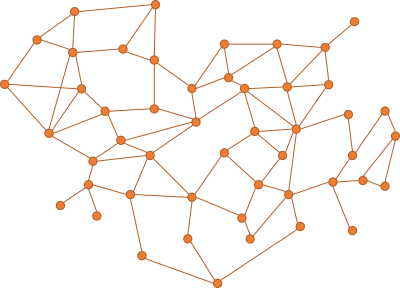
Think of each node as a unit of code; a class or a module. While a dependency graph is a directed graph, I didn't indicate the directions. Imagine that most edges point both ways, so that the nodes are interdependent. In other ways, the graph has cycles. This is not uncommon in C# code.
Pick any node in such a graph, and chances are that other nodes depend on it. This makes it hard to make changes to the code in that node, because a change may affect the code that depends on it. As you try to fix the depending code, that change, too, ripples through the network.
This already explains why tight coupling is problematic.
It is difficult to make predictions, especially about the future #
When you write source code, you might be tempted to try to take into account future needs and requirements. There may be a historical explanation for that tendency.
"That is, once it was a sign of failure to change product code. You should have gotten it right the first time."
In the days of punchcards, you had to schedule time to use a computer. If you made a mistake in your program, you typically didn't have time to fix it during your timeslot. A mistake could easily cost you days as you scrambled to schedule a new time. Not surprisingly, emphasis was on correctness.
With this mindset, it's natural to attempt to future-proof code.
YAGNI #
With interactive development environments you can get rapid feedback. If you make a mistake, change the code and observe the outcome. Don't add code because you think that you might need it later. You probably will not.
While you should avoid speculative generality, that alone is no guarantee of clean code. Unless you're careful, you can easily make a mess by tightly coupling different parts of your code base.
How do produce a code base that is as easy to change as possible?
Write code that is easy to delete #
Write code that is easy to change. The ultimate change you can make is to delete code. After that, you can write something else that better does what you need.
"A system where you can delete parts without rewriting others is often called loosely coupled"
I don't mean that you should always delete code in order to make changes, but often, looking at extremes can provide insights into less extreme cases.
When you have a tangled web as shown above, most of the code is coupled to other parts. If you delete a node, then you break something else. You'd think that deleting code is the easiest thing in the world, but it's not.
What if, on the other hand, you have smaller clusters of nodes that are independent?
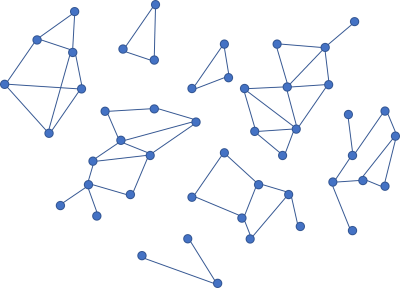
If your dependency graph looks like this, you can at least delete each of the 'islands' without impacting the other sub-graphs.
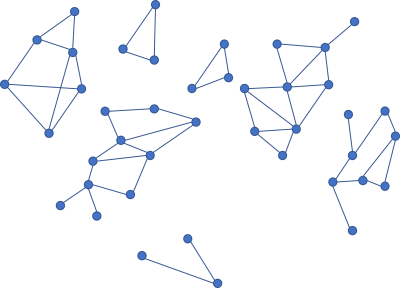
Writing code that is easy to delete may be a good idea, but even that is easier said that done. Loose coupling is, once more, key to good architecture.
Add something better #
Once you've deleted a cluster of code, you have the opportunity to add something that is even less coupled than the island you deleted.
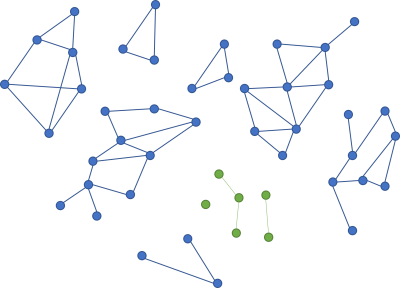
If you add new code that is less coupled than the code you deleted, it's even easier to delete again.
Conclusion #
Coupling is a key factor in code organisation. Tightly coupled code is difficult to change. Loosely coupled code is easier to change. As a thought experiment, consider how difficult it would be to delete a particular piece of code. The easier it is to delete the code, the less coupled it is.
Deleting a small piece of code to add new code in its stead is the ultimate change. You can often get by with a less radical edit, but if all else fails, delete part of your code base and start over. The less coupled the code is, the easier it is to change.
The Reader monad
Normal functions form monads. An article for object-oriented programmers.
This article is an instalment in an article series about monads. A previous article described the Reader functor. As is the case with many (but not all) functors, Readers also form monads.
This article continues where the Reader functor article stopped. It uses the same code base.
Flatten #
A monad must define either a bind or join function, although you can use other names for both of these functions. Flatten is in my opinion a more intuitive name than join, since a monad is really just a functor that you can flatten. Flattening is relevant if you have a nested functor; in this case a Reader within a Reader. You can flatten such a nested Reader with a Flatten function:
public static IReader<R, A> Flatten<R, A>( this IReader<R, IReader<R, A>> source) { return new FlattenReader<R, A>(source); } private class FlattenReader<R, A> : IReader<R, A> { private readonly IReader<R, IReader<R, A>> source; public FlattenReader(IReader<R, IReader<R, A>> source) { this.source = source; } public A Run(R environment) { IReader<R, A> newReader = source.Run(environment); return newReader.Run(environment); } }
Since the source Reader is nested, calling its Run method once returns a newReader. You can Run that newReader one more time to get an A value to return.
You could easily chain the two calls to Run together, one after the other. That would make the code terser, but here I chose to do it in two explicit steps in order to show what's going on.
Like the previous article about the State monad, a lot of ceremony is required because this variation of the Reader monad is defined with an interface. You could also define the Reader monad on a 'raw' function of the type Func<R, A>, in which case Flatten would be simpler:
public static Func<R, A> Flatten<R, A>(this Func<R, Func<R, A>> source) { return environment => source(environment)(environment); }
In this variation source is a function, so you can call it with environment, which returns another function that you can again call with environment. This produces an A value for the function to return.
SelectMany #
When you have Flatten you can always define SelectMany (monadic bind) like this:
public static IReader<R, B> SelectMany<R, A, B>( this IReader<R, A> source, Func<A, IReader<R, B>> selector) { return source.Select(selector).Flatten(); }
First use functor-based mapping. Since the selector returns a Reader, this mapping produces a Reader within a Reader. That's exactly the situation that Flatten addresses.
The above SelectMany example works with the IReader<R, A> interface, but the 'raw' function version has the exact same implementation:
public static Func<R, B> SelectMany<R, A, B>( this Func<R, A> source, Func<A, Func<R, B>> selector) { return source.Select(selector).Flatten(); }
Only the method declaration differs.
Query syntax #
Monads also enable query syntax in C# (just like they enable other kinds of syntactic sugar in languages like F# and Haskell). As outlined in the monad introduction, however, you must add a special SelectMany overload:
public static IReader<R, T1> SelectMany<R, T, U, T1>( this IReader<R, T> source, Func<T, IReader<R, U>> k, Func<T, U, T1> s) { return source.SelectMany(x => k(x).Select(y => s(x, y))); }
As already predicted in the monad introduction, this boilerplate overload is always implemented in the same way. Only the signature changes. With it, you could write an expression like this nonsense:
IReader<int, bool> r = from dur in new MinutesReader() from b in new Thingy(dur) select b;
Where MinutesReader was already shown in the article Reader as a contravariant functor. I couldn't come up with a good name for another reader, so I went with Dan North's naming convention that if you don't yet know what to call a class, method, or function, don't pretend that you know. Be explicit that you don't know.
Here it is, for the sake of completion:
public sealed class Thingy : IReader<int, bool> { private readonly TimeSpan timeSpan; public Thingy(TimeSpan timeSpan) { this.timeSpan = timeSpan; } public bool Run(int environment) { return new TimeSpan(timeSpan.Ticks * environment).TotalDays < 1; } }
I'm not claiming that this class makes sense. These articles are deliberate kept abstract in order to focus on structure and behaviour, rather than on practical application.
Return #
Apart from flattening or monadic bind, a monad must also define a way to put a normal value into the monad. Conceptually, I call this function return (because that's the name that Haskell uses):
public static IReader<R, A> Return<R, A>(A a) { return new ReturnReader<R, A>(a); } private class ReturnReader<R, A> : IReader<R, A> { private readonly A a; public ReturnReader(A a) { this.a = a; } public A Run(R environment) { return a; } }
This implementation returns the a value and completely ignores the environment. You can do the same with a 'naked' function.
Left identity #
We need to identify the return function in order to examine the monad laws. Now that this is accomplished, let's see what the laws look like for the Reader monad, starting with the left identity law.
[Theory] [InlineData(UriPartial.Authority, "https://example.com/f?o=o")] [InlineData(UriPartial.Path, "https://example.net/b?a=r")] [InlineData(UriPartial.Query, "https://example.org/b?a=z")] [InlineData(UriPartial.Scheme, "https://example.gov/q?u=x")] public void LeftIdentity(UriPartial a, string u) { Func<UriPartial, IReader<Uri, UriPartial>> @return = up => Reader.Return<Uri, UriPartial>(up); Func<UriPartial, IReader<Uri, string>> h = up => new UriPartReader(up); Assert.Equal( @return(a).SelectMany(h).Run(new Uri(u)), h(a).Run(new Uri(u))); }
In order to compare the two Reader values, the test has to Run them and then compare the return values.
This test and the next uses a Reader implementation called UriPartReader, which almost makes sense:
public sealed class UriPartReader : IReader<Uri, string> { private readonly UriPartial part; public UriPartReader(UriPartial part) { this.part = part; } public string Run(Uri environment) { return environment.GetLeftPart(part); } }
Almost.
Right identity #
In a similar manner, we can showcase the right identity law as a test.
[Theory] [InlineData(UriPartial.Authority, "https://example.com/q?u=ux")] [InlineData(UriPartial.Path, "https://example.net/q?u=uuz")] [InlineData(UriPartial.Query, "https://example.org/c?o=rge")] [InlineData(UriPartial.Scheme, "https://example.gov/g?a=rply")] public void RightIdentity(UriPartial a, string u) { Func<UriPartial, IReader<Uri, string>> f = up => new UriPartReader(up); Func<string, IReader<Uri, string>> @return = s => Reader.Return<Uri, string>(s); IReader<Uri, string> m = f(a); Assert.Equal( m.SelectMany(@return).Run(new Uri(u)), m.Run(new Uri(u))); }
As always, even a parametrised test constitutes no proof that the law holds. I show the tests to illustrate what the laws look like in 'real' code.
Associativity #
The last monad law is the associativity law that describes how (at least) three functions compose. We're going to need three functions. For the purpose of demonstrating the law, any three pure functions will do. While the following functions are silly and not at all 'realistic', they have the virtue of being as simple as they can be (while still providing a bit of variety). They don't 'mean' anything, so don't worry too much about their behaviour. It is, as far as I can tell, nonsensical.
public sealed class F : IReader<int, string> { private readonly char c; public F(char c) { this.c = c; } public string Run(int environment) { return new string(c, environment); } } public sealed class G : IReader<int, bool> { private readonly string s; public G(string s) { this.s = s; } public bool Run(int environment) { return environment < 42 || s.Contains("a"); } } public sealed class H : IReader<int, TimeSpan> { private readonly bool b; public H(bool b) { this.b = b; } public TimeSpan Run(int environment) { return b ? TimeSpan.FromMinutes(environment) : TimeSpan.FromSeconds(environment); } }
Armed with these three classes, we can now demonstrate the Associativity law:
[Theory] [InlineData('a', 0)] [InlineData('b', 1)] [InlineData('c', 42)] [InlineData('d', 2112)] public void Associativity(char a, int i) { Func<char, IReader<int, string>> f = c => new F(c); Func<string, IReader<int, bool>> g = s => new G(s); Func<bool, IReader<int, TimeSpan>> h = b => new H(b); IReader<int, string> m = f(a); Assert.Equal( m.SelectMany(g).SelectMany(h).Run(i), m.SelectMany(x => g(x).SelectMany(h)).Run(i)); }
In case you're wondering, the four test cases produce the outputs 00:00:00, 00:01:00, 00:00:42, and 00:35:12. You can see that reproduced below:
Haskell #
In Haskell, normal functions a -> b are already Monad instances, which means that you can easily replicate the functions from the Associativity test:
> f c = \env -> replicate env c > g s = \env -> env < 42 || 'a' `elem` s > h b = \env -> if b then secondsToDiffTime (toEnum env * 60) else secondsToDiffTime (toEnum env)
I've chosen to write the f, g, and h as functions that return lambda expressions in order to emphasise that each of these functions return Readers. Since Haskell functions are already curried, I could also have written them in the more normal function style with two normal parameters, but that might have obscured the Reader aspect of each.
Here's the composition in action:
> f 'a' >>= g >>= h $ 0 0s > f 'b' >>= g >>= h $ 1 60s > f 'c' >>= g >>= h $ 42 42s > f 'd' >>= g >>= h $ 2112 2112s
In case you are wondering, 2,112 seconds is 35 minutes and 12 seconds, so all outputs fit with the results reported for the C# example.
What the above Haskell GHCi (REPL) session demonstrates is that it's possible to compose functions with Haskell's monadic bind operator >>= operator exactly because all functions are (Reader) monads.
Conclusion #
In Haskell, it can occasionally be useful that a function can be used when a Monad is required. Some Haskell libraries are defined in very general terms. Their APIs may enable you to call functions with any monadic input value. You can, say, pass a Maybe, a List, an Either, a State, but you can also pass a function.
C# and most other languages (F# included) doesn't come with that level of abstraction, so the fact that a function forms a monad is less useful there. In fact, I can't recall having made explicit use of this knowledge in C#, but one never knows if that day arrives.
In a similar vein, knowing that endomorphisms form monoids (and thereby also semigroups) enabled me to quickly identify the correct design for a validation problem.
Who knows? One day the knowledge that functions are monads may come in handy.
Next: Reactive monad.

Comments
A postscript to your detective story might note that the primary NuGet cache lives at
%userprofile%\.nuget\packageson Windows and~/.nuget/packageson Mac and Linux. The folder names there are much easier to decipher than the folders and files in the http cache.